Indian Cultural Values Explorer
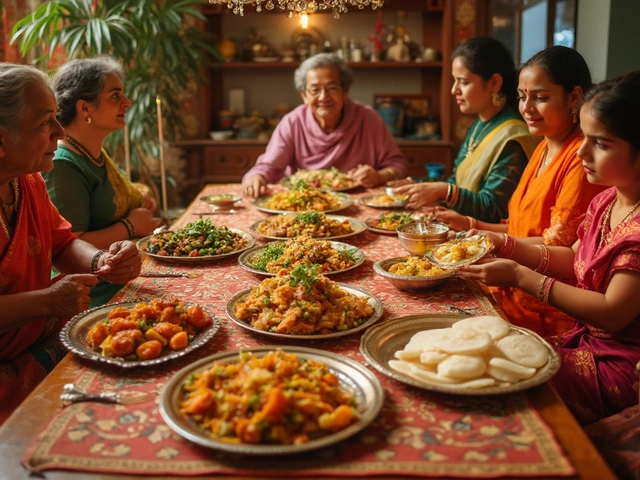
Family & Kinship
Collective support and shared responsibility
Respect for Elders
Honor through words and deeds
Spirituality & Dharma
Righteous duty and moral order
Hospitality
Guest as deity, warm welcome
Non-Violence (Ahimsa)
Peaceful coexistence and compassion
Explore Value Details
Select a value from above to see detailed information.
Cultural Values Comparison Table
| Value | Core Principle | Everyday Expression | Typical Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Family | Collective support | "Parivaar ka khayal" | Joint family sharing expenses |
| Respect for Elders | Honor through words and deeds | Touching feet for blessings | Consulting grandparents before marriage |
| Spirituality & Dharma | Righteous duty | Morning prayers, fasting | Performing puja before work |
| Hospitality | Guest as deity | Offering tea and sweets | Hosting relatives for festivals |
| Ahimsa | Non-violence to all life | Vegetarian meals, gentle speech | Choosing plant-based diet |
When you think of India, what springs to mind? Maybe bright festivals, spicy dishes, bustling markets. But beneath the colors lies a set of deeply rooted values that guide daily life. Indian culture values are a blend of ancient philosophy and modern practice, shaping how families interact, how strangers greet, and how decisions are made.
Quick Takeaways
- Family ties act as the backbone of social life.
- Respect for elders is expressed through language and behavior.
- Spirituality and dharma infuse everyday choices.
- Hospitality treats every guest like a deity.
- Ahimsa promotes non‑violence in thought and action.
1. Family & Kinship
Family in India goes beyond the nuclear unit. Extended relatives live close by, share meals, and celebrate milestones together. This deep bond creates a support network that cushions financial, emotional, and educational challenges. For instance, a child’s tuition often comes from grandparents, while younger siblings look after aging parents. The concept of "joint family" means decisions are made collectively, reinforcing the idea that individual success is tied to group well‑being.
Because of this value, you’ll hear phrases like "parivaar ka khayal" (take care of the family) in everyday conversation. In urban centers, even when families migrate abroad, they maintain regular video calls, group WhatsApp chats, and yearly reunions, proving that the family value adapts without losing its core.
2. Respect for Elders (Aadar)
Elders occupy a revered position. Respect is shown through language-using honorifics like "ji" or "Sir/Madam"-and gestures, such as touching feet ("pranams") to seek blessings. In households, seniors are consulted before major purchases or marriage decisions, reflecting the belief that experience brings wisdom.
Public spaces mirror this value too. In schools, children stand when teachers enter, and in markets, younger shoppers yield aisles to older customers. These practices reinforce social harmony and convey that age carries authority.
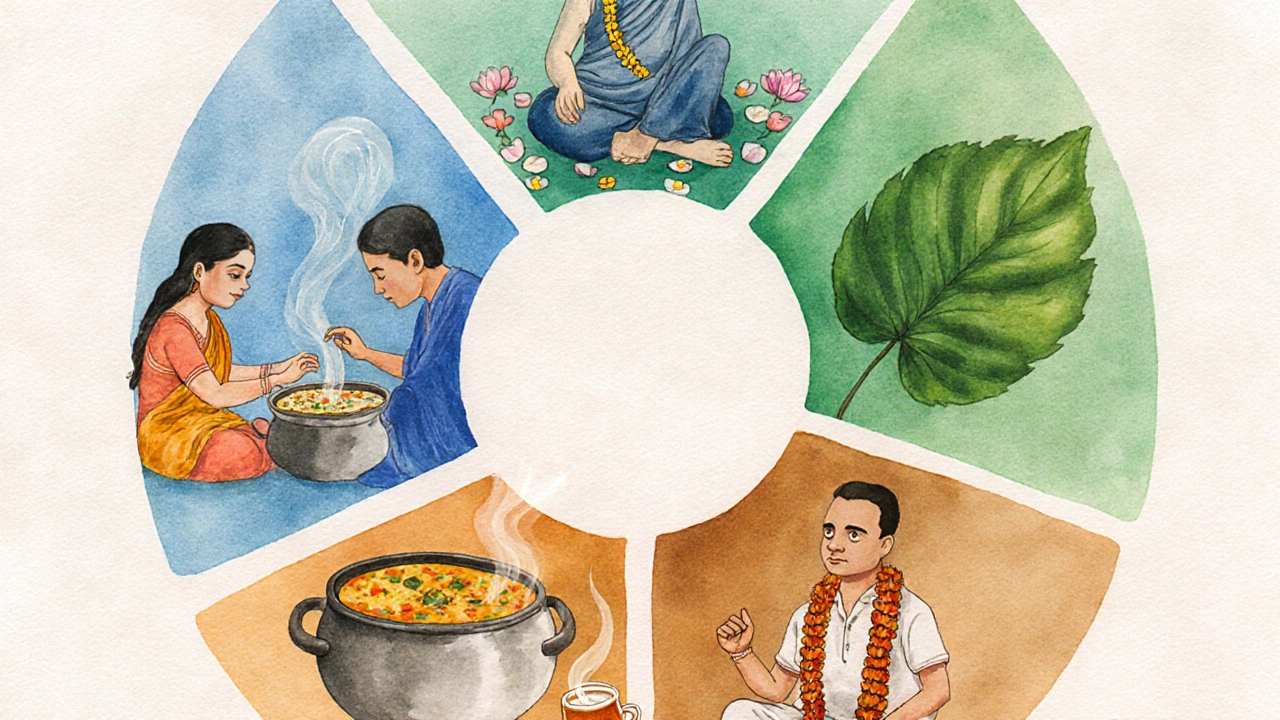
3. Spirituality & Dharma
Spirituality is woven into daily routines, whether through prayers, meditation, or festivals. The guiding principle of Dharma-righteous duty-helps individuals align personal actions with moral order. It isn’t limited to religion; it spills into work ethics, community service, and even parenting.
Typical expressions include chanting mantras before meals, lighting incense during evening prayers, or observing fasting on auspicious days. A study by the Indian Council of Social Science Research (2023) found that 78% of respondents consider spiritual practice essential for mental balance.
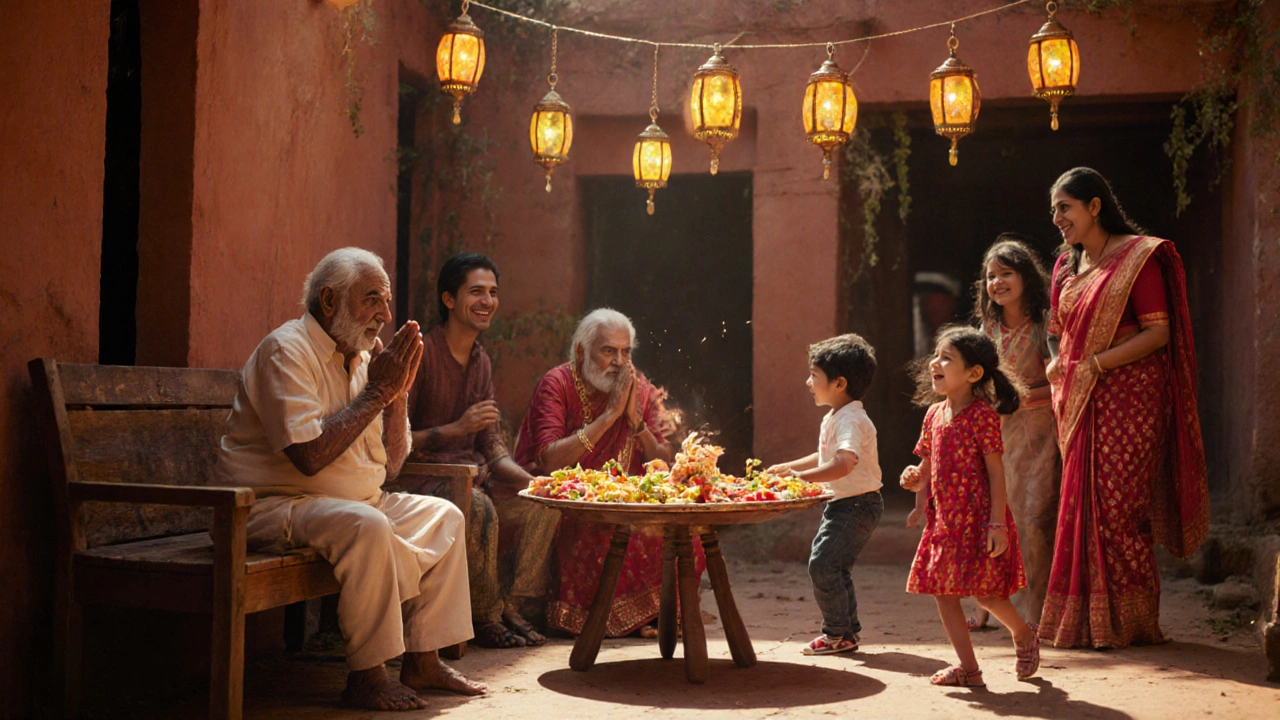

4. Hospitality - "Atithi Devo Bhava"
Hospitality in India translates to "the guest is God." Hosts go to great lengths-preparing elaborate meals, offering comfortable bedding, and ensuring guests feel honored. Even strangers encountered on a train may be offered water or a seat.
This value fuels the vibrant hospitality industry, from homestays in Kerala to street food vendors who greet travelers with a smile and a serving of chai. It also underpins social cohesion, as sharing food creates bonds that transcend caste, class, or language.
5. Non‑Violence (Ahimsa)
Ahimsa-the principle of non‑violence-was popularised by Mahatma Gandhi, but its roots stretch back to ancient Jain and Buddhist teachings. It guides behavior toward people, animals, and the environment.
Practically, Ahimsa appears in vegetarian diets, animal‑friendly festivals, and conflict‑resolution methods that prioritize dialogue over force. Recent data from the Ministry of Environment (2024) shows a 12% rise in vegetarian households across urban India, reflecting a growing embrace of this value.
Comparison of the Five Core Values
| Value | Core Principle | Everyday Expression | Typical Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Family | Collective support | "Parivaar ka khayal" | Joint family sharing expenses |
| Respect for Elders | Honor through words and deeds | Touching feet for blessings | Consulting grandparents before marriage |
| Spirituality & Dharma | Righteous duty | Morning prayers, fasting | Performing puja before work |
| Hospitality | Guest as deity | Offering tea and sweets | Hosting relatives for festivals |
| Ahimsa | Non‑violence to all life | Vegetarian meals, gentle speech | Choosing plant‑based diet |
Why These Values Matter Today
Modern India grapples with rapid urbanisation, technology, and global influences. Yet these five values act as cultural anchors, helping people navigate change without losing identity. They foster social cohesion, reduce conflict, and encourage sustainable living-benefits that extend beyond borders.
For diaspora communities, preserving these values creates a bridge between heritage and host‑country culture, offering a sense of belonging while enriching multicultural societies.
Frequently Asked Questions
What role does family play in everyday Indian life?
Family acts as the primary social unit, offering emotional, financial, and educational support. Decisions-ranging from career moves to marriage-are often discussed with extended relatives, ensuring that individual choices align with collective well‑being.
How is respect for elders shown in Indian households?
Respect is expressed through language (using honorifics like "ji"), gestures such as touching the feet for blessings, and by seeking elders’ opinions before major decisions. Younger members also prioritize caring for aging parents as a duty.
Can non‑violence really influence modern Indian society?
Yes. Ahimsa drives the growth of vegetarianism, animal‑friendly festivals, and peaceful protest movements. Government data shows a steady rise in plant‑based consumption, and many NGOs use non‑violent advocacy to promote environmental policies.
What does "Atithi Devo Bhava" mean for visitors?
The phrase translates to "the guest is God". Hosts make extraordinary effort to ensure comfort-offering food, a clean space, and warm greetings-so visitors feel honoured and respected.
How does spirituality influence daily routines?
Spirituality manifests through morning prayers, mantra recitation, and observing fasts on auspicious days. These practices provide mental clarity, reinforce moral duties (dharma), and connect individuals to a larger cultural narrative.





Write a comment